In today’s interconnected global economy, the food distribution industry is the backbone ensuring that consumers worldwide have access to a diverse array of products. However, this intricate network faces numerous challenges that can disrupt the seamless flow from producers to consumers. Recent events have underscored the vulnerability of this sector. To navigate such complexities, businesses must adopt comprehensive contingency planning. This involves proactive risk assessment, strategic resource allocation, and the implementation of robust insurance solutions to safeguard against unforeseen disruptions. By doing so, companies can enhance their resilience, ensuring continuity and reliability in delivering food products to markets worldwide.
Navigating Supply Chain Risks
Global food supply chains are intricate networks susceptible to disruptions such as logistical delays, supplier inconsistencies, and geopolitical tensions. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, long-distance food supply chains experienced significant disruptions, adversely affecting urban consumers and farmers alike. Implementing comprehensive risk management strategies, including diversifying suppliers and routes, is crucial. Insurance solutions like Stock Throughput Insurance offer coverage from origin to destination, safeguarding against potential losses.
Ensuring Business Continuity
Unforeseen events—natural disasters, political upheavals, or pandemics—can disrupt operations. Developing a robust crisis management plan that identifies specific risks and outlines clear communication strategies is vital.
Analyzing recent insurance claims in the food industry highlights key areas of risk that businesses must prepare for. Auto or trailer incidents accounted for 28% of claims, making transportation-related disruptions the most common financial liability. Accident-causing third-party damage followed at 18%, demonstrating how external factors can significantly impact supply chain operations. Additionally, theft (13%) and equipment failure or food spoilage (13%) were major contributors to financial losses, further emphasizing the importance of proper risk management strategies.
Other claims, including unforeseen operational failures and logistical issues, collectively made up 28% of reported incidents, reinforcing the need for comprehensive contingency planning.
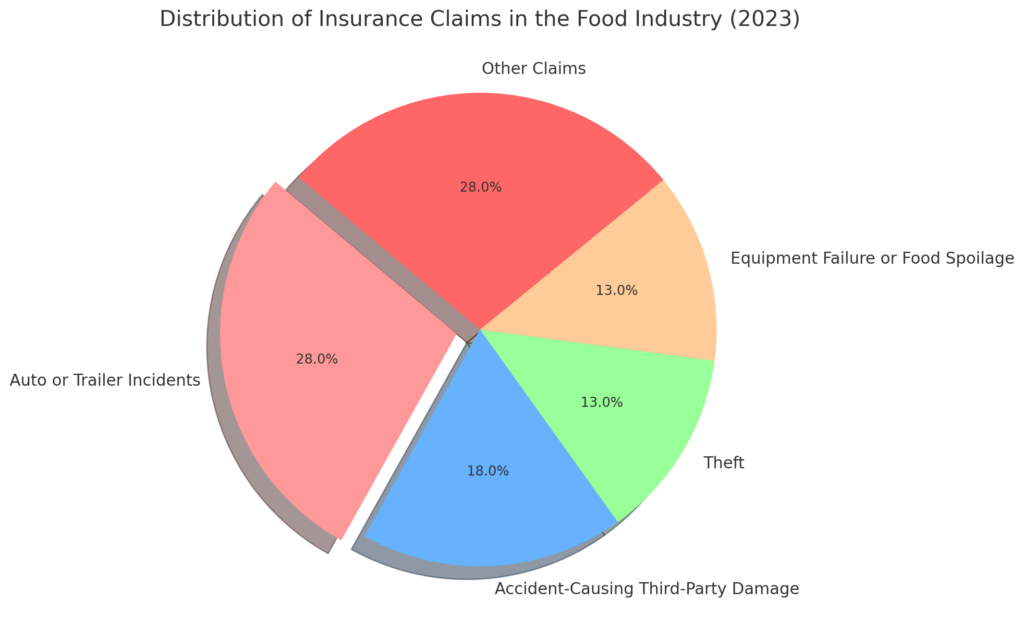
Source: https://riskandinsurance.com/flip-report-reveals-economic-and-claims-trends-in-food-industry/
These statistics underscore the necessity of business interruption insurance, cargo coverage, and supply chain risk management to mitigate financial losses and maintain operational continuity in the face of disruptions. Business Interruption Insurance can mitigate financial losses during such disruptions, ensuring operational stability.
Maintaining Food Safety and Compliance
Safety concerns, including contamination and spoilage, pose significant risks. Adhering to international regulations and standards is non-negotiable. The European Commission’s contingency plan aims to ensure a sufficient and varied supply of safe, nutritious, affordable, and sustainable food to citizens at all times. Food Safety Insurance provides financial protection against incidents like product recalls, while Regulatory Defense and Penalties Insurance covers expenses related to compliance breaches.
Protecting Against Cyber Threats
The digitalization of the food industry has increased vulnerability to cyberattacks. In 2024, Stop & Shop experienced product shortages in some of its 350 Northeast U.S. stores due to a cybersecurity incident that disrupted supply-chain. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential. Cyber Liability Insurance offers coverage for data breaches and operational disruptions, safeguarding digital assets and sensitive information.
Strategic Vendor Management
Strong relationships with suppliers are foundational to a resilient supply chain. Conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining clear communication can prevent disruptions. In 2024, the USDA faced food shortages affecting tribes and low-income seniors due to a shift to a single distributor. Product Liability Insurance and Supply Chain Insurance protect against risks arising from vendor-related issues.
Discover Essential Insurance Insights with Us!
Since 1947, Coughlin Insurance has steadfastly stood by distributors, importers, and exporters, ensuring they are protected against the unpredictable nature of the food trade industry. As specialists who understand the nuances and vulnerabilities of the global food distribution network, we’ve fine-tuned insurance solutions to cater to this industry’s evolving dynamics. Our affiliations with the Association of Food Industries (AFI), National Frozen & Refrigerated Foods Association (NFRA), and the Peanut And Tree Nut Processors Association (PTNPA), reinforce our commitment to safeguarding your business with unparalleled expertise. We ask you to consider a partnership where understanding meets action.
You may have been recommended to us by one of our many satisfied customers, or you may have searched online for “Food industry insurance.” However you found us, we’re happy to welcome you. To discuss your needs and objectives and how we can help your company, please contact JJ Van Aman, Vice President of Sales email: jj@coughlinis.com tel: 973-598-5884 or reach out for a free insurance quote today!
Sources we have researched to generate content in this article:
https://www.bonadio.com/news-events/articles/managing-risks-in-the-food-beverage-industry; https://blog.safetychain.com/risk-management-food-beverage-companies;
https://www.specpage.com/risk-management/;
https://tandobeverage.com/business-risks-in-food-and-beverage-industry/; https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/mitigating-top-5-risks-food-beverage-sector-rajendran-m/; https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/risk/us-risk-final-food-safety-eerm-pov.pdf
